The how is sales tax calculated statement of retained earnings is closely connected to other financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. Retained earnings are typically a component of the equity section on the balance sheet, and they can be affected by the net income reported in the income statement. Additionally, events like dividend payments, which are part of cash flows, can impact the statement of retained earnings. Retained earnings play a crucial role in a company’s financial health and have a significant impact on the shareholders’ equity.
Understanding the Statement
- Calculating the ending retained earnings isn’t just a mere formality—it’s a powerful indicator of economic endurance and fiscal foresight.
- The other half of the profits are considered retained earnings because this is the amount of earnings the company kept or retained.
- Should your company decide to pay dividends, the exact amount you distribute nibbles away at the net income’s contribution to retained earnings.
- This account serves as a measure of the company’s ability to generate profit, reinvest, and create value for shareholders.
- This statement is often used to prepare before the statement of stockholder’s equity because retained earnings is needed for the overall ending equity calculation.
This can lead to an increase in the stock price and can help to attract new investors. This money can be used for various purposes, including expanding the business, paying off debt, or funding research and development. External reporting requirements also involve incorporating certain disclosure mandates from regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). By carefully considering these factors, companies can create an effective capital allocation strategy that maps out the best use of their the statement of retained earnings retained earnings to support growth and maximize shareholder value. Retained earnings are primarily used for reinvestment into the company, funding new projects, R&D, expansion, reducing debts, or as a reserve for future opportunities or unexpected expenses.

Statement Retained Earnings: Essential Guide for Financial Success
- It provides insight into the company’s financial health, as the increased retained earnings demonstrate its ability to keep profits for future use.
- Companies may assign par value to their shares to give confidence to investors that the shares cannot be issued at a later time to other investors below the par value.
- Fundamental financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement play a key role in evaluating a company’s performance.
- The title of your statement of retained earnings should include your company name, the title of the financial statement (Statement of Retained Earnings), and the time period it covers.
- Let’s take a fictional company, XYZ Corp., to illustrate the preparation of a Retained Earnings Statement.
- Understanding this helps them see the full financial picture and keeps expectations about dividend policies and company valuation in check.
Calculating the ending retained earnings solidifies your company’s financial narrative, reflecting both past decisions and setting the stage for future investments or debt management. It’s a number that tells a story, so make sure it’s penned with precision and clarity. The plot behind this step revolves around the outcome of your business’s operations. Revenue is nothing but a high-five until you subtract the costs it took to rack up those sales.
- This can make a business more appealing to investors who are seeking long-term value and a return on their investment.
- Generally, companies like to have positive net income and positive retained earnings, but this isn’t a hard-and-fast rule.
- On the other hand, when a company experiences growth in its retained earnings, it often indicates a reinvestment of profits into the business or potential for future dividend payments.
- It is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate sales and it’s reported before deducting any expenses.
- The net income amount in the above example is the net profit line item, which is $115,000.
Share this article

Conversely, cash on hand is the literal liquid assets—currency, bank account balances, easily accessible funds—that a company can quickly mobilize for immediate needs, emergencies, or opportunities. Remember, you might have a mountain of retained earnings and still run into daily cash flow issues if that money is tied up elsewhere. It reassures shareholders about the company’s health, aligns them with management’s vision, and often, keeps them invested for the long haul.
Deduct Dividend Payments
It demonstrates a balanced approach to managing earnings that can be conducive to sustainable growth. To ensure you have a crystal-clear understanding of the retained earnings calculation process, let’s walk through Zippy Tech’s example, step by step. So, $14,500 would be the final figure to strut onto your balance sheet, ready to roll into the next period’s retained earnings calculation. Dividends are the slices of the profit pie that shareholders eagerly await, representing a reward for their investment in your company. But bear in mind, this isn’t a compulsory tradition; some companies choose to reinvest profits back into the business instead. Your company could decide to reinvest the earnings back into the business instead.


Once you’ve settled on the starting line with the beginning balance, you’re ready to turn up the heat with the core element of retained earnings – your net income (or sometimes, alas, the net loss). Visualize this process as setting the stage before the hustle and bustle of business activities come into play, ensuring that the starting line is clearly marked. The beginning balance is your financial anchor, and from here, you’ll navigate through the fiscal ebbs and flows to chart the course of your retained earnings. Remember, your beginning balance isn’t just an arbitrary number; it embodies the company’s cumulative earnings minus cumulative dividends since day one.
Statement of retained earnings formula
- Here’s how to show changes in retained earnings from the beginning to the end of a specific financial period.
- Retained earnings are profits not paid out to shareholders as dividends; that is, they are the profits the company has retained.
- The company retains the money and reinvests it—shareholders only have a claim to it when the board approves a dividend.
- It’s no wonder that savvy investors keep an eagle eye on this part of your balance sheet — it tells them whether the company is an able custodian of their investment.
- From the question, we were not given the shares issued during the current reporting period.
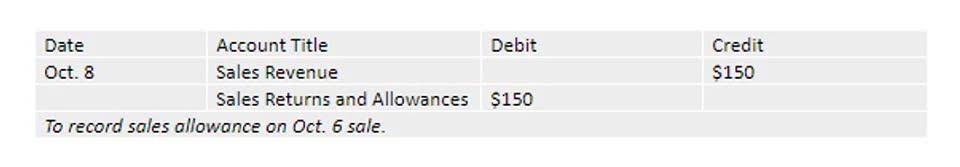
The statement of retained earnings reconciles the beginning-of-period balance of retained earnings to the end-of-period balance. The net income or loss for the period is used to calculate the change in retained earnings. Dividends paid during the period are deducted from net income to arrive at the change in retained earnings.

If the company has a negative net income or a loss, it has incurred expenses exceeding Retail Accounting its revenue and has no earnings to keep. Whether you are a business owner, accountant, or simply interested in financial reporting, this overview will provide a comprehensive explaination of the Statement of Retained Earnings. Let’s say your business has beginning retained earnings of $10,000 and net income of $4,000. Retained earnings are typically used for reinvesting in the company, funding growth opportunities, repaying debt, purchasing assets, or building a reserve against future losses. Walking through this example, it’s evident that Zippy Tech is maintaining a healthy cycle of profit reinvestment while also rewarding its shareholders.